Comprehensive guide on how to overclock CPU safely outlines the steps, handy free tools and how to avoid overheating the CPU.
Those who make the PC’s CPU work harder can expect a little more performance. But be careful: Too much is unhealthy. We explain what overclocking is all about and how you can tease a few more megahertz out of your computer without overheating.
Find more technology guides, tips and advice
CONTENTS
What is overclocking
What are the dangers of overclocking?
How to overclock CPU: Engage the turbo – but do it right!
Manually overclocking
The turbo function
Extended perspective
Slowly approach the perfect value
Windows boots slowly, games stutter and Photoshop can’t keep up? Then it’s time to step up a gear. Overclocking is the magic word. With a few tools and a little patience, you may be able to get your computer into the fast lane. But how does it work and what does overclocking actually mean?
Well, it basically just means that you put more stress on the processor. The CPU works faster than the manufacturer intended. This gives you more computing power without having to invest in new hardware. However, a faster hard drive – such as an SSD – can also accelerate the boot process. And gamers often benefit from a more modern graphics card in order to tease out one or the other picture per second in demanding and fast-paced 3D action.
If you only need your computer for the office and the web anyway, you don’t even need to worry about overclocking. The effects would be hardly or not at all noticeable, so you probably don’t need to know how to overclock the CPU.
An overclocked CPU is more suitable for challenging desktop applications such as Adobe Photoshop or video editing programs such as Sony’s Catalyst. This type of software relies on powerful computing cores for numerous tasks and therefore benefits more from an overclocked processor.
What is overclocking?
In addition to the data transfer rate, the clock frequency is one of the decisive variables for how fast a CPU can handle the computing processes required for data processing. This clock frequency is usually specified by the manufacturer and specified in the product specifications of the CPU. However, this value usually does not reflect the maximum performance of the processor. It is chosen so that it meets the requirements of most users and at the same time supports the best possible energy efficiency and service life of the CPU.
But what if the clock frequency of the CPU is not sufficient for your personal usage behavior? This can happen, for example, if you use powerful programs and raw data formats for photo and video editing or if you are an avid gamer. Then you don’t have to think about replacing the CPU right away, but can manually increase the clock frequency of the CPU to improve the computing power – i.e. overclock the processor. This designation comes about because the originally intended clock frequency is deliberately exceeded, so this is where it is useful to know how to overclock a CPU safely.
Incidentally, overclocking is not only possible with the CPU, but with all PC components that work with a periodic clock signal – for example also with the graphics card or the main memory. If you operate all hardware components coordinated with one another at a higher clock frequency, you can significantly increase the system performance of your PC.
What are the dangers of overclocking the CPU?
Before you go straight to the action, you should make yourself aware that your PC functions as an overall system. If you change individual parameters, this also affects other components. The most important thing is that you create the conditions for good cooling, because when you overclock your PC, more heat is inevitably generated . To protect against overheating, the system throttles the power (i.e. the clock frequency) as soon as the sensors report temperatures above the specified limit values. This is exactly what you don’t want when overclocking the CPU. So ensure good cooling from the outset by either increasing the speed of the built-in cooler or retrofitting a powerful external cooling system (e.g. with water or nitrogen).
Another source of danger is the increased voltage . Make sure that the power supply can withstand these values or increase the voltage only as far as the technical specifications allow. In general, we recommend that you initially only achieve the increase in performance by increasing the clock rates. Increasing the voltage brings significantly more power, but stresses the respective components so much that the service life usually decreases significantly.
How to overclock CPU: Engage the turbo – but do it right!
Manufacturer Intel, for example, equips its Core i7 series with processors that are particularly easy to overclock. These can be recognized by the “K” in the name. These models have what is known as an open multiplier. The clock frequency can be changed in a targeted manner. However, for overclocking, the right motherboard on which the processor sits must also play a role. You can find out whether your motherboard is suitable for this or whether the BIOS or UEFI may need to be updated in the mainboard manual.
If you have made the correct settings in the BIOS, you can expect increased computing power. However, more power also means more heat. But don’t worry: an expensive water or even helium cooling is not necessary for a gradual and careful overclocking.
Nevertheless, one should cautiously approach the adventure of overclocking. If you overdo it, in the worst case scenario, the computer will literally smoke.
The chip manufacturers plan a lower clock rate for their processors right from the start. So the core won’t start to melt right away just because you push it to do a little more. The Intel Core i7 7700K CPU, for example, works with a frequency of 4.2 GHz. If you overclock the chip, it still runs stably up to 4.8 GHz. A gain of at least 600 megahertz. However, no two computing cores are the same. Even identical CPUs of the same model series can vary in the overclocking results.
How to overclock CPU: Manually overclocking
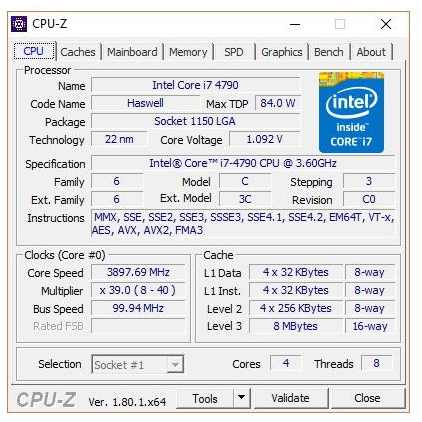
The CPU-Z tool provides an overview of all information about the processor.
Your computer is a bit older, but you still want to make it work? No problem. With just a few small settings, you can get a little more performance out of almost any processor. But first a little preparation is necessary: Download the free Windows programs HWinfo64 , Prime95 and CPU-Z down.

HWinfo65 provides a quick overview of all hardware components.
The former tells you the processor temperature. Monitoring the heat development is essential later on. Prime95, on the other hand, is a simple tool for calculating prime numbers. The best thing about it: The software calculates the math problems with a specially optimized code for the processor. The CPU is significantly more demanding than in everyday tasks – an ideal stress test for freshly overclocked cores.
Finally, install CPU-Z. This program shows you all the information about your processor that is important. This includes information such as voltage to the second, clock frequency and much more. Everything installed? Then it’s down to business: Go to the BIOS or UEFI of your mainboard (usually by pressing the “DEL” or “F12” keys during the boot process). Here you turn on three different options.
For overclocking, both the multiplier for the clock rate of the processor, the core voltage of the processor and the so-called Load Line Calibration (LLC for short) must be changed and coordinated. Incidentally, the latter ensures that the voltage of the processor corresponds to that which the CPU takes in normal desktop operation, even under load.
How to overclock CPU: The turbo function
The clock frequency of a CPU is made up of the front side bus (an important interface on the processor, which specifies the clock rate of all components addressed, FSB for short) and the multiplier. For example, a computing core with 4 GHz works with an FSB with 400 MHz, which the multiplier multiplies ten times. In order to save their customers from fiddling around with hardware and BIOS, the manufacturers supply some of their processors with a turbo function.
The Turbo Boost Technology of modern processors is a kind of dynamic overclocking function: It stimulates the processor to the preset performance as soon as the operating system demands the highest possible power. The i7 7700K, for example, then automatically turns up to a pre-configured 4.5 GHz.
How to overclock CPU: Extended perspective
You don’t see these points? Then you may have to set the view in the UEFI or BIOS to an expert mode in order to find the professional settings. Every motherboard has its own BIOS, so a closer look at the manual can tell you exactly where to find the above settings.
First turn off the processor booster or turbo. Since we are now driving the CPU to higher performance ourselves, we no longer need this help in the BIOS. Next, set the Load Line Calibration to a medium value, e.g. B. 4.
Next, adjust the voltage on the processor and set it to the recommended value for your model. With modern processors such as the Intel competitor AMD Ryzen 5 1600 this is 1.35 volts.
The last thing we need is the correct multiplier. You set this under the clock frequency or “CPU Frequency” in 100 megahertz steps. To stay with the example of the Ryzen 5 1600, this would be a multiplier of 36 – i.e. 3.6 GHz. This corresponds to the maximum clock frequency in the turbo mode of the processor. First note down the standard values so that you can undo everything in the event of instability. Save the changes in the UEFI or BIOS and restart the computer.
Slowly approach the perfect value
As soon as Windows has started up, start the programs Prime95, HWinfo64 and CPU-Z. The first stress test should now begin. To do this, click on “Just stress test” in the Prime95 welcome window and click on “Custom” on the left. Enter the value 1344 under “Torture settings” for the items Min FFT size and Max FFT size. This way the processor is fully loaded. After clicking on “Ok”, the ultimate test for the overclocked CPU begins.
Now at the latest, keep an eye on the temperature in the HWinfo64 program: Start the tool, then click on “Sensors only” and scroll down. The hottest core shouldn’t get over 82 degrees. Cancel Prime95 if it gets too hot.
If the prime number calculation runs stably for half an hour, the computer does not crash and no other problems arise, you can reboot the computer into the BIOS and start the process from the beginning. Gradually increase the values until you get the most out of your performance.
The clock rate can be found in the CPU-Z program during the prime stress test. You can find detailed overclocking instructions for various motherboard-CPU combinations under overclocking.guide .
By the way: Everyone has to find the perfect combination of voltage, LLC and multiplier for their own system. Feel your way forward carefully to get your computer moving with targeted overclocking.




